In this article we’ll look at the aptly named Pricing Strategy Matrix. Yes, we know… There seems to be a 2×2 matrix for everything! But to be fair, pricing is a difficult subject, so often any help is more than welcome!
Let’s take a look in more detail…
What is the Pricing Strategy Matrix?
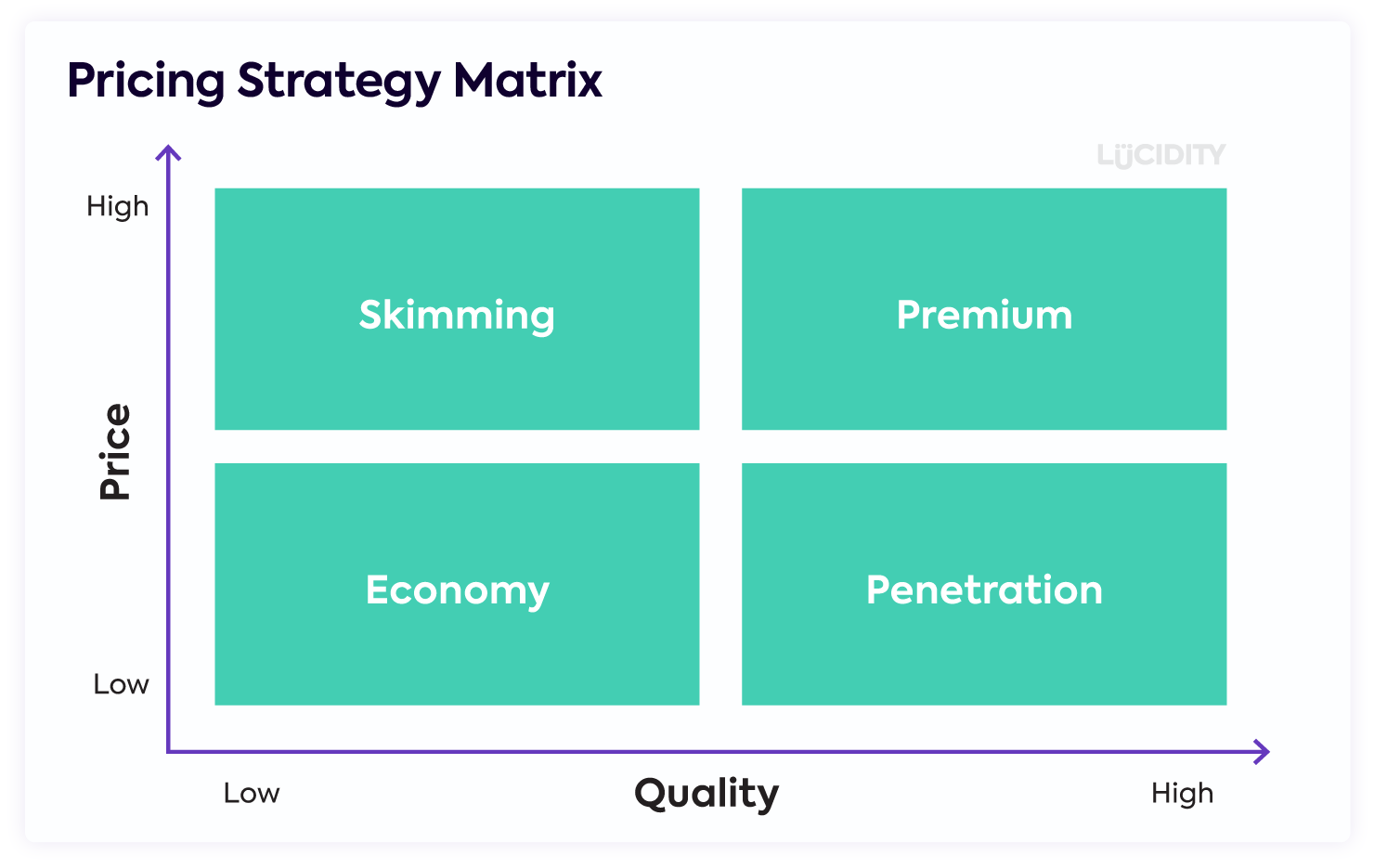
The Pricing Strategy Matrix is a tool that helps companies decide the best price for a product or service by looking at both the price and the quality and highlighting four potential strategic options.
As the above shows, there are four strategies/segments that are used in this matrix:
- Skimming
- Premium
- Economy
- Penetration
Each of these is a different approach to pricing in a market with an associated set of pros and cons.
What is the Skimming Price Strategy?
Skimming as a pricing strategy is where your price point is initially high when compared to your product quality. The goal is to get as many customers to buy it at the high margin price before you begin to decrease.
Each time you decrease the price point you are targeting a different segment of the market who will be prepared to pay the new amount.
Skimming can be used for product or service launches as a way to maximise the amount of revenue from a small number of customers.
Examples of Price Skimming:
- Games consoles often launch at a higher price point
- New phones
- Blu-ray releases of films/TV
Advantages of Price Skimming:
- Highest margin generated per customer
- Can increase perception of quality
- Each decrease in price should increase sales
- No race to the bottom
Disadvantages of Price Skimming:
- Competitor activity can move quickly to undercut your price
- Negative brand perception of price being too high for customers
- Reduced sales potential
- Easy to get wrong
What is the Premium Price Strategy?
If you’re operating a high quality product or service for a high price, then Premium Price may be the strategy for you. As the name suggests, this strategy is all about maintaining a high price point in the market and, crucially, maintaining the perception of a premium product or service to justify that price.
Examples of Premium Pricing:
- Apple products
- Designer clothing
- Certain supermarkets (e.g. Waitrose in the UK)
Advantages of Premium Pricing:
- Very high margins can be obtained
- Positive brand perception of high quality
- Often high customer satisfaction due to the perception
Disadvantages of Premium Pricing:
- Difficult to maintain
- Pressure to innovate and keep up quality
- Big target for cheaper competitors
- Difficult to regain if lost
- Sales can underperform in times of economic difficulties
What is the Economy Price Strategy?
The opposite to Premium is Economy, when your quality and price point are both deemed to be low. It’s a form of Competitive Based Pricing mixed with Cost Plus Pricing, where you go for being the lowest price point in the market and undercut any competitors.
Examples of Economy Pricing:
- Aldi or Lidl in the UK market
- Budget airlines such as JetBlue in the US market
Advantages of Economy Pricing:
- Rapid market share is possible
- Can cause problems for competitors who cannot price match
- Can be used as a gateway product or service to others with higher price points
Disadvantages of Economy Pricing:
- Difficult to create good margins
- Can be hard to maintain
- Can ignite a race to the bottom between competitors
- Can damage brand perception
What is the Penetration Price Strategy?
Penetration Pricing is a strategy where your product or service is high quality but your price point is low. It’s often used as an introduction to a market, a way to increase sales initially by making it a ‘no brainer’ before migrating to a different form of strategy such as Premium or Skimming. The price point decided for entry will often take into account competitors, making this also a form of Competitor Based Pricing.
Examples of Penetration Price Strategy:
- New phone contracts or utility suppliers
- Any ‘special launch offer’ pricing
Advantages of Penetration Price Strategy:
- Can boost initial sales
- Can cause a marketing buzz and higher demand
- Increases market awareness for consumers
Disadvantages of Penetration Price Strategy:
- Lower margins initially
- Longer time to recoup costs of launching product or service
- Sets an anchored price point in consumers’ minds
Can companies use more than one strategy at a time in the Pricing Strategy Matrix?
Yes, you might be a company with multiple products or services and so each of those may have it’s own pricing strategy. You may also use certain pricing strategies at certain times, for example launching with Penetration before moving to Premium, or going from Premium to Skimming / Economy.
What are the advantages of the Pricing Strategy Matrix?
The Pricing Strategy Matrix has a number of advantages:
- It’s easy to understand and quick to use
- It provides four pricing discussion points
- It’s suitable for all markets/industries
What are the limitations of the Pricing Strategy Matrix?
There are some limitations with the model, most notably:
- It’s very simplistic and pricing is a complicated subject
- The options are not granular
- It can be difficult to judge the opinion of quality
What are the alternatives to the Pricing Strategy Matrix?
The biggest alternative to the Pricing Strategy Matrix is Kotler’s Pricing Strategies. Kotler produced a list of potential pricing strategies for a market, some of which match this more simplistic matrix.
What tools complement the Pricing Strategy Matrix?
The tools that go well with the Pricing Strategy Matrix are:
This is a simple framework that enables businesses to step back from just a price point and think about the entire revenue model, including all aspects of how you generate income and value.
There are three commonly used methods to set a price point:
Each method is helpful in shaping a potential price point.
The Five Forces model looks at the different impacts on your potential profitability in a market, ranging from buyers and suppliers, through to substitution, threat of new entry, and the overall competitive marketplace.