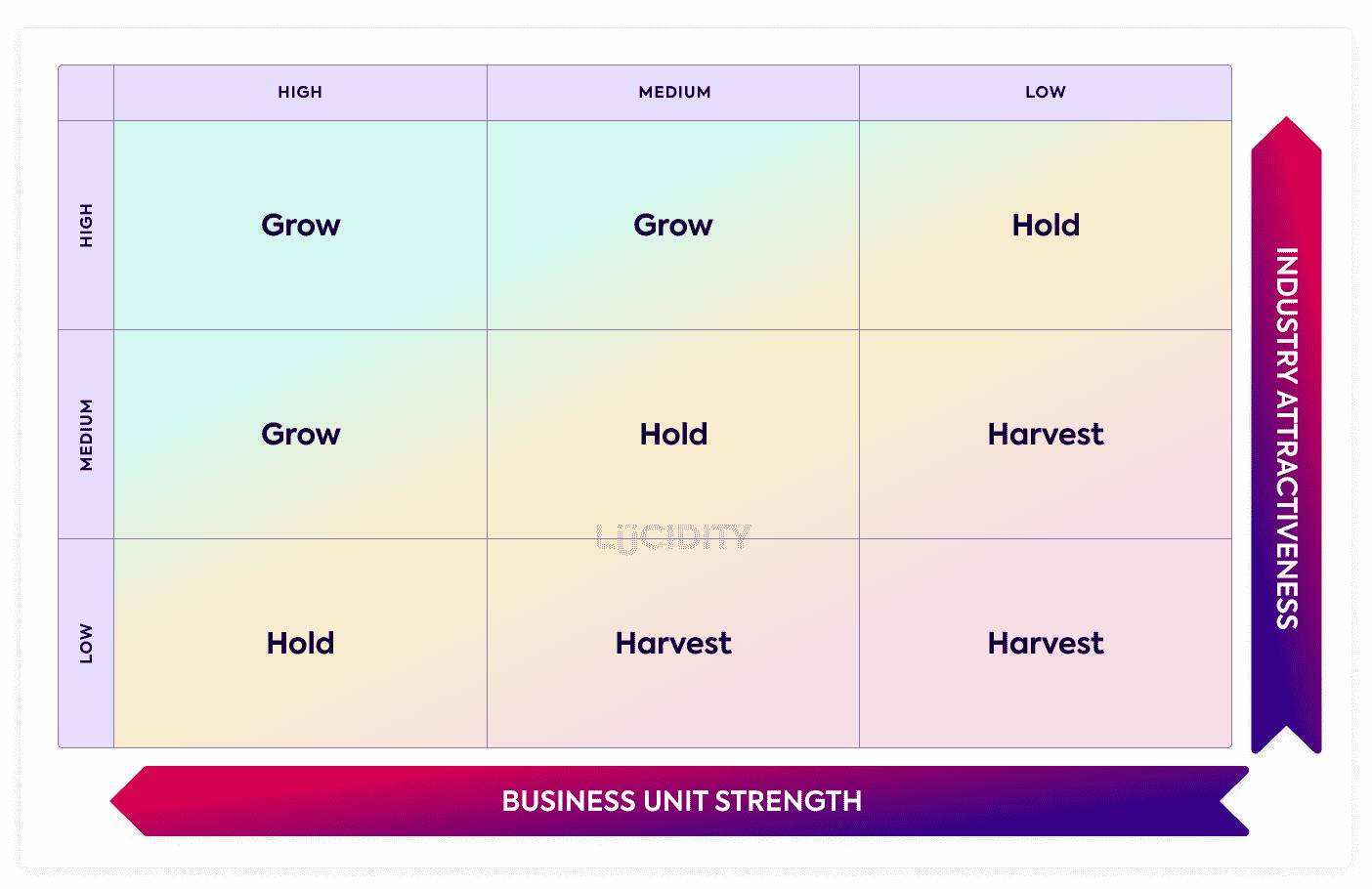
The GE Matrix is a 3×3 matrix designed to help you decide where your investment for resources should be within a business. You can think of it as similar to the arguably more famous BCG Matrix, in that you allocate products produced by the SBU (Strategic Business Units) or activities within each box, in order to determine future actions.
Let’s take a look in more detail…
What is The GE Matrix?
The GE Matrix is a 3×3 tool that allows you to map different products, services or activities based on the attractiveness of the industry and the strength of the business unit.
The matrix helps you decide the appropriate investment strategies between the following options:
Grow/Invest: Activities placed in this area should be invested as you have a high strength in a highly attractive industry.
Hold: Activities that land within this section are less appealing for investment than the Grow activities, but not necessarily at the point of exiting.
Harvest/Divest: If activity is weak in strength and the industry is not attractive then it’s likely one you should consider exiting or closing down.
Now it’s important to note that these are guides not gospel, so keep in mind you’ve got to consider the wider factors and future potential of your business unit, market, and industry structure.
What is Industry Attractiveness?
Industry attractiveness is a measurement of how easy it would be for you to have success within the market and establish a competitive position. The more profitability potential in your market then the more attractive it is for the company.
Some of the elements you should consider:
- Market growth rate and growth projection over a long period of time
- Market size and existing players
- Five Forces of the market (suppliers, buyers, entry, substitution, rivalry)
- Lifecycle of the market
- Wider environmental issues using PESTLE
Also worth noting is:
- Attractive does not mean there is necessarily a low cost of entry
- Attractive does not mean there is necessarily similarities between it and your current market
You can find out more about attractiveness by looking at Porter’s Three Tests.
What is Business Unit Strength?
Business Unit Strength is a measurement of how effective your current business unit is in the market. This can be subjective, but there are ways to help evaluate the performance. Consider the following:
- Current market share
- Rate of growth compared to competitors and competitive advantage
- Market perception of your product or service
- Brand reputation
- Customer churn rates
- Sales win / lose reasons
- Your competitive advantages
- Profitability
It can helpful to look at VRIO framework as part of this process.
How do you measure Industry Attractiveness in the GE Matrix?
It is important to be able to distinguish an unattractive industry from its counterpart.
Industry attractiveness is measured by looking at the market size, market growth, potential profitability, and future projection of the industry. Tools such as Five Forces, Six Forces and PESTLE are commonly used.
A similar concept is used in Porter’s Three Tests, one of which is establishing how attractive an industry is in order to decide upon a diversification strategy.
How do you measure Business Unit Strength in the GE Matrix?
Measuring Business Unit Strength comes down to looking at the results, so consider your market share, your rate of growth, unique selling point, or sustainable competitive advantages, the brand reputation and the profit margins. Partnerships and channels may also play a role in determining the strength.
What are the advantages of the GE Matrix?
The advantages of GE Matrix are:
- It provides a method to establish which activities in a business should get investment
- It is a simple tool to show the whole business portfolio in one image
- It is more detailed than alternatives such as the BCG Matrix
- It fits with all businesses and is easy to use
What are the disadvantages of the GE Matrix?
Some disadvantages and limitations include:
- The decisions around attractiveness and strength can be subjective
- It requires a lot of market data in order to map out the results, which for a company with a diverse portfolio can be an extensive task
- Business units may support multiple products and be different strengths in each
- Some of the strategic implications might not align with the company’s core values
What are the alternatives to the GE Matrix?
One alternative to the GE Matrix is the BCG Matrix.
Who invented the GE Matrix?
The GE matrix was first developed by McKinsey for General Electric in the 1970s, building on the work from the BCG Matrix.