Michael Porter is one of the most famous academics in the world of strategy, developing numerous models over the years. Five Forces is probably his most famous and is really useful when you need to evaluate a marketplace.
What is the Porter’s Five Forces framework?
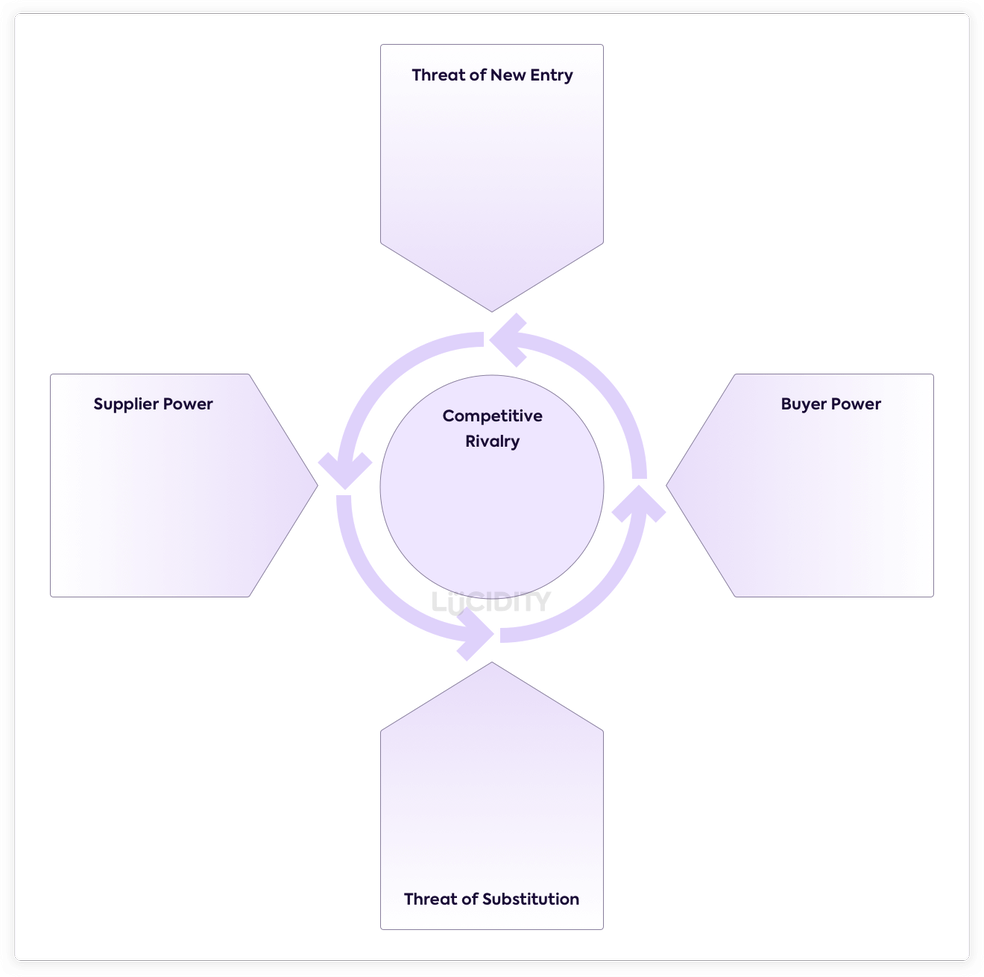
Five Forces is a framework to analysis and understand the forces that are shaping your competitive marketplace. It’s a framework to look at your industry not your company. It covers many areas such as the dynamics of the customers, the power of suppliers, the risk you’ll be substituted with a different product or service, the different direct competitors and the risk of new entry to the market.
The structure above shows the external factors pushing into your competitive market, as well as acknowledging the different players within this space.
What is each force in Porter’s Five Forces?
The five forces are:
Power of Buyers:
This force is all about your customers and their ability to drive your price down or your overall direction. It is impacted by how many customers you have, how significant they are, what the cost of acquisition is, and what relationships are in place with customers.
Power of Suppliers:
Any business uses suppliers to provide a service or product. It might be material to produce clothing, or it could be a hosting provider like AWS for a software company. These suppliers have a direct impact on your business – so this power looks at what influence they can have on your pricing. How many suppliers are in the market, what are your options, what is the relationship with your suppliers like?
Risk of Substitutes:
What would it take to replace your product or service with an alternative? This isn’t about customers going to competitors – we’ll come to that! – it’s about an alternative to what you provide being offered in the market. Factors such as if there are substitutes currently available, what would the cost of using them be to customers, and if you see substitutes growing as a trend can all be considered here.
Risk of New Entrants:
Some markets are harder to enter than others, and this force considers how easy it might be for you to suddenly find new competition arising within your customer base. Consider the time and cost it takes to enter the market, what barriers are in place that protect you from companies entering? A common mistake is to just consider startups, but reality is that startups are just one factor in new entry. You must consider both start-ups and existing businesses diversifying. Did Hotmail consider Google a new entry threat prior to Gmail existing?
Competitive Rivalry:
This is the most commonly considered force, that of the existing competition to your product or service. How many providers are in your space? What is the differentiation between them? How does it influence your power and pricing? Your sales team will be best placed to feed into this force.
What are the advantages of Porter’s Five Forces?
Five Forces has a number of advantages:
- It’s simple to understand and use
- It covers a lot of specific issues that directly relate to your growth
- It’s an easy but comprehensive
- You can do it on your own, as a team in person, or as a group remotely
- It provides a better overview of your competition
What are some of the limitations of Porter’s Five Forces?
Five Forces is a great tool for marketplace analysis but you need to consider:
- There’s no analysis of your business, it’s purely external
- There are no actions out of this framework
- It’s a short term analysis where the information can rapidly change
- It’s a high level view on the marketplace
- There are no factors outside of the market being considered
How do you make the most out of Porter’s Five Forces?
Five Forces remains a popular framework for reviewing the marketplace and identifying potential growth opportunities and threats.
There are three golden rules to follow before you begin Five Forces:
- Prepare for the session by researching the latest news on competitors
- Defining the marketplace you intend to analyse
- Be equipped with the information of why previous customers have left you
What preparation should be done before a Porter’s Five Forces?
To get the most effective Five Forces outcome, it is helpful to have knowledge of:
- Detail on why customers have left your product or service in the past
- Latest news in your chosen sector
- Any competitive activity your aware of
If you’ll be doing Five Forces in a group, remember to share this information in advance.
How can I create my own Porter’s Five Forces?
We’ve written this guide on how to create a Porter’s Five Forces model especially to answer this question!
Who invented Porter’s Five Forces?
Michael Porter invented Five Forces, first publishing the model in Harvard Business Review in May 1979. Yes, that’s the same Michael Porter who invented Porter’s Generic Strategies, Porter’s Three Tests and more…!
What’s the best medium for running a Porter’s Five Forces based session?
Like many of these frameworks, Five Forces works best when done in a group. Given the focus is on the marketplace your group should include senior sales, marketing or product individuals who are up to speed on the latest developments.
How often should we update our Porter’s Five Forces model?
Five Forces can become out of date more frequently than other models because it relies so heavily on what is being done by other companies. Given this we often see FF used when making strategic decisions about market entry, and thus only being updated once a year. If you’re using Five Forces in a way to regularly make business decisions, then you should consider a quarterly update.